


Every house has a unique architectural style, and sometimes it has two or more. Renovations and new, eclectic mixes make fitting a home into one specific category daunting or even impossible. Thankfully, there’s no need to memorize complicated architectural terminology. REALTOR® Magazine has compiled a guide to common residential architectural styles. Read about the details that give a home character, history, and romance.

The 1925 Paris Exhibition Internationale des Arts Decoratifs launched the Art Deco style, which echoed the Machine Age with geometric decorative elements and a vertically oriented design. This distinctly urban style was never widely used in residential buildings; it was more widespread in public and commercial buildings of the period.
Towers and other projections above the roofline enhance the vertical emphasis of this style, which was popularized by Hollywood movies of the 1930s. Flat roofs, metal window casements, and smooth stucco walls with rectangular cut-outs mark the exteriors of Art Deco homes. Facades are typically flush with zigzags and other stylized floral, geometric, and “sunrise” motifs. By 1940 the Art Deco style had evolved into “Art Moderne,” which features curved corners, rectangular glass-block windows, and a boat-like appearance. Popularized in the United States by Finnish architect Eliel Saarinen, the style enjoyed a revival in the 1980s.

These narrow, rectangular one and one-half story houses originated in California during the 1880s as a reaction to the elaborate decoration of Victorian homes. The style then moved eastward to the Midwest in the early 20th century, where it remained popular until the Great Depression. Bungalows have low-pitched gabled or hipped roofs and small covered porches at the entry. The style became so popular that you could order a bungalow kit from Sears and Roebuck catalog. The name “bungalow” had its origins in India, where it indicated a small, thatched home.

Some of the first houses built in the United States were Cape Cods. The original colonial Cape Cod homes were shingle-sided, one-story cottages with no dormers. During the mid-20th century, the small, uncomplicated Cape Cod shape became popular in suburban developments. A 20th-century Cape Cod is square or rectangular with one or one-and-a-half stories and steeply pitched, gabled roofs. It may have dormers and shutters. The siding is usually clapboard or brick.
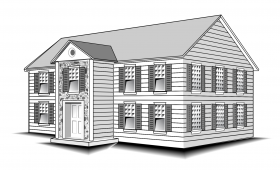
America’s colonial period encompassed a number of housing types and styles. For more information about Colonial styles, see Cape Cod, Saltbox, Georgian, and Dutch Colonial. However, when we speak of the Colonial style, we often are referring to a rectangular, symmetrical home with bedrooms on the second floor. The double-hung windows usually have many small, equally sized square panes.
During the late 1800s and throughout the 20th century, builders borrowed Colonial ideas to create refined Colonial Revival homes with elegant central hallways and elaborate cornices. Unlike the original Colonials, Colonial Revival homes are often sided in white clapboard and trimmed with black or green shutters.

You know them by their odd-sized and often tall windows, their lack of ornamentation, and their unusual mixtures of wall materials—stone, brick, and wood, for instance. Architects designed Contemporary-style homes (in the Modern family) between 1950 and 1970, and created two versions: the flat-roof and gabled types. The latter is often characterized by exposed beams. Both breeds tend to be one-story tall and were designed to incorporate the surrounding landscape into their overall look.

Popularized at the turn of the 20th century by architect and furniture designer Gustav Stickley in his magazine, The Craftsman, the Craftsman-style bungalow reflected, said Stickley, “a house reduced to it’s simplest form… its low, broad proportions and absolute lack of ornamentation gives it a character so natural and unaffected that it seems to… blend with any landscape.”
The style, which was also widely billed as the “California bungalow” by architects such as Charles Sumner Greene and Henry Mather Greene, featured overhanging eaves, a low-slung gabled roof, and wide front porches framed by pedestal-like tapered columns. Material often included stone, rough-hewn wood, and stucco. Many homes have wide front porches across part of the front, supported by columns.

The Creole Cottage, which is mostly found in the South, originated in New Orleans in the 1700s. The homes are distinguished by a front wall that recedes to form a first-story porch and second-story balcony that stretch across the entire front of the structure. Full-length windows open into the balconies, and lacy ironwork characteristically runs across the second-story level. These two- and three-story homes are symmetrical in design with front entrances placed at the center.
“Creole French,” a variation of the basic Creole design, came into vogue in southern states in the 1940s and 1950s.

This American style originated in homes built by German, or “Deutsch” settlers in Pennsylvania as early as the 1600s. A hallmark of the style is a broad gambrel roof with flaring eaves that extend over the porches, creating a barn-like effect. Early homes were a single room, and additions were added to each end, creating a distinctive linear floor plan. End walls are generally of stone, and the chimney is usually located on one or both ends. Double-hung sash windows with outward swinging wood casements, dormers with shed-like overhangs, and a central Dutch double doorway are also common. The double door, which is divided horizontally, was once used to keep livestock out of the home while allowing light and air to filter through the open top. The style enjoyed a revival during the first three decades of the 20th century as the country looked back with nostalgia to its colonial past.

Ubiquitous up and down the East Coast, Federal-style architecture dates from the late 1700s and coincided with a reawakening of interest in classical Greek and Roman culture. Builders began to add swags, garlands, elliptical windows, and other decorative details to rectangular Georgian houses. The style that emerged resembles Georgian, but is more delicate and more formal. Many Federal-style homes have an arched Palladian window on the second story above the front door. The front door usually has sidelights and a semicircular fanlight. Federal-style homes are often called “Adam” after the English brothers who popularized the style.

Balance and symmetry are the ruling characteristics of this formal style. Homes are often brick with detailing in copper or slate. Windows and chimneys are symmetrical and perfectly balanced, at least in original versions of the style. Defining features include a steep, high, hip roof; balcony and porch balustrades; rectangle doors set in arched openings; and double French windows with shutters. Second-story windows usually have a curved head that breaks through the cornice.
The design had its origins in the style of rural manor homes, or chateaus, built by the French nobles during the reign of Louis XIV in the mid-1600s. The French Provincial design was a popular Revival style in the 1920s and again in the 1960s.

Befitting a king—in fact, the style is named for four King Georges of England—Georgian homes are refined and symmetrical with paired chimneys and a decorative crown over the front door. Modeled after the more elaborate homes of England, the Georgian style dominated the British colonies in the 1700s. Most surviving Georgians sport side-gabled roofs, are two to three stories high, and are constructed in brick. Georgian homes almost always feature an orderly row of five windows across the second story. Modern-day builders often combine features of the refined Georgian style with decorative flourishes from the more formal Federal style.

The influence of English romanticism and the mass production of elaborate wooden millwork after the Industrial Revolution fueled the construction of Gothic Revival homes in the mid-1800s. These picturesque structures are marked by “Gothic” windows with distinctive pointed arches; exposed framing timbers; and steep, vaulted roofs with cross-gables. Extravagant features may include towers and verandas. Ornate wooden detailing is generously applied as gable, window, and door trim.
American architects Alexander Jackson Davis and Andrew Jackson Downing championed Gothic in domestic buildings in the 1830s. Most Gothic Revival homes were constructed between 1840 and 1870 in the Northeast.
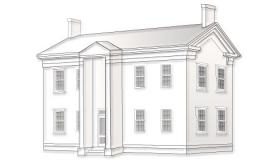
This style is predominantly found in the Midwest, South, New England, and Midatlantic regions, though you may spot subtypes in parts of California. Its popularity in the 1800s stemmed from archeological findings of the time, indicating that the Grecians had spawned Roman culture. American architects also favored the style for political reasons: the War of 1812 cast England in an unfavorable light; and public sentiment favored the Greeks in their war for independence in the 1820s.
Identify the style by its entry, full-height, or full-building width porches, entryway columns sized in scale to the porch type, and a front door surrounded by narrow rectangular windows. Roofs are generally gabled or hipped. Roof cornices sport a wide trim. The front-gable found in one subtype became a common feature in Midwestern and Northeastern residential architecture well into the 20th century. The townhouse variation is made up of narrow, urban homes that don’t always feature porches. Look for townhouses in Boston, Galveston, Texas., Mobile, Ala., New York, Philadelphia, Richmond, Va., and Savannah, Ga.

Initiated by European architects—such as Mies van der Rohe—in the early 20th century, this is the style that introduced the idea of exposed functional building elements, such as elevator shafts, ground-to-ceiling plate glass windows, and smooth facades.
The style was molded from modern materials—concrete, glass, and steel—and is characterized by an absence of decoration. A steel skeleton typically supports these homes. Meanwhile, interior and exterior walls merely act as design and layout elements, and often feature dramatic, but nonsupporting projecting beams and columns. With its avant-garde elements, naturally the style appeared primarily in the East and in California.

Italianate homes, which appeared in Midwest, East Coast, and San Francisco areas between 1850 and 1880, can be quite ornate despite their solid square shape. Features include symmetrical bay windows in front; small chimneys set in irregular locations; tall, narrow, windows; and towers, in some cases. The elaborate window designs reappear in the supports, columns, and door frames.

This style emerged in 1853 when Boston merchant Thomas Larkin relocated to Monterey, Calif. The style updates Larkin’s vision of a New England Colonial with an Adobe brick exterior. The Adobe reflected an element of Spanish Colonial houses common in the Monterey area at the time. Later Monterey versions merged Spanish Eclectic with Colonial Revival styles to greater or lesser extents.
Larkin’s design also established a defining feature of Montereys: a second-floor with a balcony. At the time one-story homes dominated the Bay Area.
In today’s Montereys, balcony railings are typically styled in iron or wood; roofs are low pitched or gabled and covered with shingles—variants sometimes feature tiles—and exterior walls are constructed in stucco, brick, or wood.
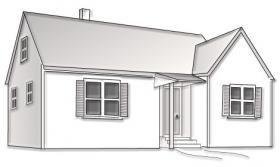
Born out of the fundamental need for shelter, National-style homes, whose roots are set in Native American and pre-railroad dwellings, remain unadorned and utilitarian. The style is characterized by rectangular shapes with side gabled roofs or square layouts with pyramidal roofs. The gabled-front-and-wing style pictured here is the most prevalent type with a side-gabled wing attached at a right angle to the gabled front. Two subsets of the National style, known as “hall-and-parlor family” and “I-house,” are characterized by layouts that are two rooms wide and one room deep. Massed plan styles, recognized by a layout more than one room deep, often sport side gables and shed-roofed porches. You’ll find National homes throughout the country.

A well-publicized, world-class event can inspire fashion for years. At least that’s the case with the 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago, which showcased cutting-edge classical buildings that architects around the country emulated in their own residential and commercial designs. The Neoclassical style remained popular through the 1950s in incarnations from one-story cottages to multilevel manses. Its identifying Ionic or Corinthian columned porches often extend the full height of the house. Also typical: symmetrical facades, elaborate, decorative designs above and around doorways, and roof-line balustrades (low parapet walls).

In suburban Chicago in 1893, Frank Lloyd Wright, America’s most famous architect, designed the first Prairie-style house, and it’s still a common style throughout the Midwest. Prairie houses come in two styles—boxy and symmetrical or low-slung and asymmetrical. Roofs are low-pitched, with wide eaves. Brick and clapboard are the most common building materials. Other details: rows of casement windows; one-story porches with massive square supports; and stylized floral and circular geometric terra-cotta or masonry ornamentation around doors, windows, and cornices.

Taking its cues from Native American and Spanish Colonial styles, chunky looking Pueblos emerged around 1900 in California, but proved most popular in Arizona and New Mexico, where many original designs still survive.
The style is characterized by flat roofs, parapet walls with round edges, earth-colored stucco or adobe-brick walls, straight-edge window frames, and roof beams that project through the wall. The interior typically features corner fireplaces, unpainted wood columns, and tile or brick floors.

A sub-style of the late Victorian era, Queen Anne is a collection of coquettish detailing and eclectic materials. Steep cross-gabled roofs, towers, and vertical windows are all typical of a Queen Anne home. Inventive, multistory floor plans often include projecting wings, several porches and balconies, and multiple chimneys with decorative chimney pots.
Wooden “gingerbread” trim in scrolled and rounded “fish-scale” patterns frequently graces gables and porches. Massive cut stone foundations are typical of period houses. Created by English architect Richard Norman Shaw, the style was popularized after the Civil War by architect Henry Hobson Richardson and spread rapidly, especially in the South and West.

Sometimes called the California ranch style, this home in the Modern family, originated there in 1930s. It emerged as one of the most popular American styles in the 1950s and 60s, when the automobile had replaced early 20th-century forms of transportation, such as streetcars.
Now mobile homebuyers could move to the suburbs into bigger homes on bigger lots. The style takes its cues from Spanish Colonial and Prairie and Craftsman homes, and is characterized by its one-story, pitched-roof construction, built-in garage, wood or brick exterior walls, sliding and picture windows, and sliding doors leading to patios.
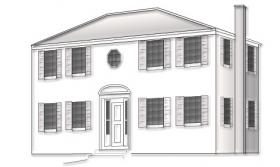
Although they borrow from the Georgian’s classic lines, Regency homes eschew ornamentation. They’re symmetrical, two or three stories, and usually built in brick. Typically, they feature an octagonal window over the front door, one chimney at the side of the house, double-hung windows, and a hip roof. They’ve been built in the United States since the early 1800s.

This New England Colonial style got its name because the sharply sloping gable roof that resembled the boxes used for storing salt. The step roofline often plunges from two and one-half stories in front to a single story in the rear. In Colonial times, the lower rear portion was often used as a partially enclosed shed, which was oriented north as a windbreak. These square or rectangular homes typically have a large central chimney and large, double-hung windows with shutters. Exterior walls are made of clapboard or shingles. In the South this style is known as a “cat’s slide” and was a popular in the 1800s.

Popular in the Midwest and Northeast, this Victorian style was fashionable for public buildings during Ulysses S. Grant’s presidency, but its elaborate, costly detail fell out of favor in the late 1800s for economic reasons. Second empire homes feature windows, molded cornices, and decorative brackets under the eaves. One subtype sports a rectangular tower at the front and center of the structure.

A subset of the Modern style, Shed homes were particular favorites of architects in the 1960s and 1970s. They feature multiple roofs sloping in different directions, which creates multigeometric shapes; wood shingle, board, or brick exterior cladding; recessed and downplayed front doorways; and small windows. There’s virtually no symmetry to the style.

This American style originated in cottages along the trendy, wealthy Northeastern coastal towns of Cape Cod, Long Island, and Newport in the late 19th century. Architectural publishers publicized it, but the style was never as popular around the country as the Queen Anne. Shingle homes borrow wide porches, shingles, and asymmetrical forms from the Queen Anne.
They’re also characterized by unadorned doors, windows, porches, and cornices; continuous wood shingles; a steeply pitched roof line; and large porches. The style hints at towers, but they’re usually just extensions of the roof line.

Tradition has it that if you fire a shotgun through the front doorway of this long, narrow home, the bullet will exit directly through the back door. The style is characterized by a single story with a gabled roof. Shotguns are usually only one room wide, with each room leading directly into the next. Exterior features include a vent on the front gable and a full front porch trimmed with gingerbread brackets and ornamentation. Mail-order plans and parts for shotgun homes were widely available at the turn-of-the-century, making it a popular, low-cost structure to build in both urban and suburban settings.
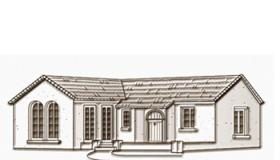
Most common in the Southwest and Florida, Spanish-style architecture takes its cues from the missions of the early Spanish missionaries—such as the one at San Juan Capistrano in California—and includes details from the Moorish, Byzantine, Gothic, and Renaissance architectural styles. The houses usually have low-pitched tiled roofs, white stucco walls, and rounded windows and doors. Other elements may include scalloped windows and balconies with elaborate grillwork, decorative tiles around doorways and windows, and a bell tower or two.

A Modern style that architects created to sequester certain living activities–such as sleeping or socializing–split levels offered an multilevel alternative to the ubiquitous style in the 1950s. The nether parts of a typical design were devoted to a garage and TV room; the midlevel, which usually jutted out from the two-story section, offered “quieter” quarters, such as the living and dining rooms; and the area above the garage was designed for bedrooms.
Found mostly in the East and Midwest, split-levels, like their Ranch counterparts, were constructed with various building materials.

A member of the Victorian family, the Stick house boasts a lot of detailing. However, few Stick homes incorporate all the possible features. Typical characteristics include gabled, steeply pitched roofs with overhangs; wooden shingles covering the exterior walls and roof; horizontal, vertical, or diagonal boards–the “sticks” from which it takes its name–that decorate the cladding; and porches.
You’ll find traditional sticks in the Northeast and their sister, the Western Stick, in California. The Western Stick is rectangular with sliding glass doors, a small chimney, and large panes of glass.

This architecture style was popular in the 1920s and 1930s and continues to be a mainstay in suburbs across the United States. The defining characteristics are half-timbering on bay windows and upper floors, and facades that are dominated by one or more steeply pitched cross gables. Patterned brick or stone walls are common, as are rounded doorways, multi-paned casement windows, and large stone chimneys. A subtype of the Tudor Revival style is the Cotswold Cottage. With a sloping roof and a massive chimney at the front, a Cotswold Cottage may remind you of a picturesque storybook home.

Victorian architecture dates from the second half of the 19th century, when America was exploring new approaches to building and design.
Advancements in machine technology meant that Victorian-era builders could easily incorporate mass-produced ornamentation such as brackets, spindles, and patterned shingles. The last true Victorians were constructed in the early 1900s, but contemporary builders often borrow Victorian ideas, designing eclectic “neo-Victorians.” These homes combine modern materials with 19th century details, such as curved towers and spindled porches. A number of Victorian styles are recreated on the fanciful “Main Street” at Disney theme parks in Florida, California, and Europe.

 Facebook
Facebook
 X
X
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Copy Link
Copy Link


